
openModeller id: GARP
Current version: 3.3 Developer(s): Ricardo Scachetti Pereira
Accepts Categorical Maps: no
Requires absence points: yes
Author(s): Stockwell, D. R. B., modified by Ricardo Scachetti Pereira
GARP is a genetic algorithm that creates ecological niche models for species. The models describe environmental conditions under which the species should be able to maintain populations. For input, GARP uses a set of point localities where the species is known to occur and a set of geographic layers representing the environmental parameters that might limit the species' capabilities to survive. This implementation is a complete rewrite of the DesktopGarp code, and it also contains the following changes/improvements: (1) Gene values changed from integers (between 1 and 253) to floating point numbers (between -1.0 and 1.0). This avoids precision problems in environment values during projection (for example, if an environment variable has the value 2.56 in some raster cell and 2.76 in another one, DesktopGarp rounds them off to 3). (2) Atomic rules were removed since they seem to have little significance compared to the other rules. (3) Heuristic operator parameters (percentage of mutation and crossover per iteration) are now static since they used to converge to fixed values during the very first iterations. This implementation simply keeps the converged values. (4) A bug was fixed in the procedure responsible for ordering the rules. When a rule was only replacing another, it was being included in the wrong position.
Stockwell, D. R. B. 1999. Genetic algorithms II. Pages 123-144 in A. H. Fielding, editor. Machine learning methods for ecological applications. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston. Stockwell, D. R. B., and D. P. Peters. 1999. The GARP modelling system: Problems and solutions to automated spatial prediction. International Journal of Geographic Information Systems 13:143-158. Stockwell, D. R. B., and I. R. Noble. 1992. Induction of sets of rules from animal distribution data: A robust and informative method of analysis. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation 33:385-390.
Max generations
openModeller id: MaxGenerations
Maximum number of iterations (generations) run by the Genetic Algorithm.
Data type: integer Domain: [1.0, oo] Typical value: 400
Convergence limit
openModeller id: ConvergenceLimit
Data type: real Domain: [0.0, 1.0] Typical value: 0.01
Population size
openModeller id: PopulationSize
Maximum number of rules to be kept in solution.
Data type: integer Domain: [1.0, 500.0] Typical value: 50
Resamples
openModeller id: Resamples
Number of points sampled (with replacement) used to test rules.
Data type: integer Domain: [1.0, 100000.0] Typical value: 2500
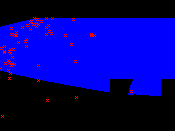
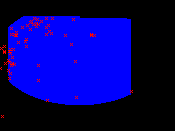
Since GARP is a non-deterministic algorithm, it produces a different result each time it runs with the same input. The following images show models in the environmental space (temperature x precipitation) generated with the same input (Thalurania furcata boliviana localities dataset) using the default parameters.
 |  |  |
| fig. 1: model 1 | fig. 2: model 2 | fig. 3: model 3 |